We all know following the best Hamstring exercises is essential for overall leg strength, stability, and athletic performance. Thus, you may be searching over the internet what are the Best Hamstring Exercises to improve your lower body strength and overall fitness.
If that’s the case, you don’t need to look further elsewhere. It’s because we have covered all your best exercise options that can help you achieve your goal with this article.
So let’s get started…
Table of contents
MORE keyboard_double_arrow_down LESS keyboard_double_arrow_up
What are hamstring muscles?
The hamstring muscle group is located at the back of the thigh and consists of three individual skeletal muscles: the Biceps femoris, Semitendinosus, and Semimembranosus. These muscles originate from the ischial tuberosity, a bony prominence in the pelvis, and extend down the thigh, crossing the hip and knee joints and inserting onto the lower leg bones (the tibia and fibula).
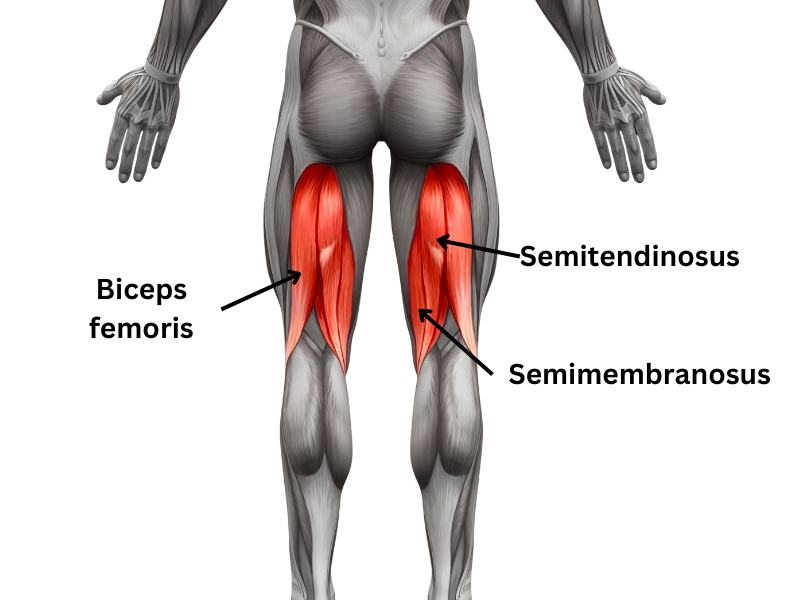
The primary functions of the hamstring muscles include:
- Flexing the knee (bending the knee joint),
- Extending the hip (moving the thigh backwards),
- Assisting in rotational movements of the knee and hip joints.
They are heavily involved in activities such as walking, running, jumping, squatting and perform many other leg movements.
These muscles also play a crucial role in stabilizing the pelvis and lower body during movement and contribute to overall lower body strength and stability.
Weakness or imbalance in the hamstring muscles can lead to
- Decreased athletic performance,
- Increased risk of injury,
- Postural issues.
Therefore, it is important to include exercises that target the hamstrings in a well-rounded fitness routine.
What are the Benefits of Having Strong Hamstring Muscles?
Strong hamstring muscles offer numerous benefits for overall health, athletic performance, and daily activities.
Some of the key benefits include:
- Improved Athletic Performance: Strong hamstrings are essential for athletes participating in sports that involve running, jumping, and explosive movements. They contribute to speed, power, agility, and overall athletic performance.
- Reduced Risk of Injury: Strong hamstrings help stabilize the knee and hip joints, reducing the risk of injuries such as strains, sprains, and tears. They also help prevent overuse injuries and imbalances that can occur due to weak or underdeveloped muscles.
- Enhanced Lower Body Strength: Strong hamstrings contribute to overall lower body strength and muscular balance. They work in conjunction with other lower body muscles, such as the quadriceps and glutes, to support various movements and activities.
- Improved Posture and Alignment: Well-developed hamstrings help maintain proper posture and alignment of the pelvis and lower back. This can reduce the risk of lower back pain and postural issues caused by muscular imbalances.
- Better Functional Movement: Strong hamstrings are essential for performing daily activities such as walking, climbing stairs, bending, and lifting objects. They contribute to functional movement patterns and make these tasks easier and more efficient.
- Enhanced Flexibility and Range of Motion: Strengthening the hamstrings can improve flexibility and range of motion in the hips and knees. This can be beneficial for activities that require a greater range of motion, such as dancing, yoga, and martial arts.
- Aesthetic Benefits: Well-defined and toned hamstrings can improve the appearance of the legs, contributing to a balanced and proportionate physique. Strengthening the hamstrings can help create a more sculpted and defined lower body.
- Reduced Risk of Falls: Strong hamstrings contribute to lower body stability and balance, reducing the risk of falls and related injuries, especially in older adults.
Overall, having strong hamstring muscles is essential for optimal health, performance, and injury prevention. Therefore, incorporating exercises that target the hamstrings into a well-rounded fitness routine can help you gain these benefits and improve your overall quality of life.
After doing a number of research and practice trials, here is our list of the Best Hamstring Exercises that are worth including in your daily exercise routine.
Best 10 Hamstring Exercises: Strengthen Your Lower Body and Improve Performance
Explore our expertly curated list of the Best 10 hamstring exercises to enhance your lower body strength, athletic performance, and muscle definition. Each exercise is accompanied by detailed explanations and execution tips to ensure effective training.
Let’s dive in and take your hamstring training to the next level!
1. Romanian Deadlifts (RDLs)
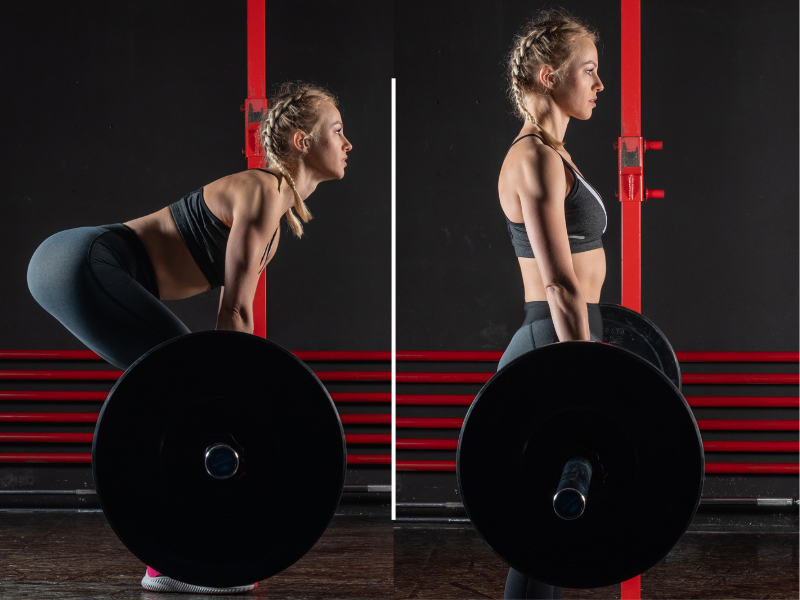

Romanian Deadlifts (RDLs) are a fundamental exercise for targeting the hamstrings, glutes, and lower back. They involve a hip hinge movement pattern, placing a greater emphasis on the hamstrings compared to conventional deadlifts.
How To Do Romanian Deadlifts (RDLs)?
- Stand with feet hip-width apart, holding a barbell or dumbbells in front of your thighs.
- Keeping your back flat and chest up, hinge at the hips while slightly bending your knees.
- Lower the weight towards the ground by pushing your hips back until you feel a stretch in your hamstrings.
- Keep the weight close to your body and maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement.
- Once you reach the bottom position, squeeze your glutes and hamstrings to return to the starting position.
Execution Tips Enhanced:
- Focus on maintaining tension in the hamstrings throughout the entire range of motion.
- Keep your back flat and avoid rounding your spine.
- Control the descent of the weight to maximize muscle activation.
Why It Works Explained:
Romanian Deadlifts target the hamstrings by placing them in a stretched position during the eccentric (lowering) phase of the movement. The hip hinge movement pattern emphasizes hip extension, which is primarily driven by the hamstrings.
Additionally, RDLs allow for a greater range of motion compared to conventional deadlifts, leading to increased muscle activation and growth in the hamstrings.
2. Glute-Ham Raises
Glute-Ham Raises are an effective bodyweight exercise for isolating the hamstrings and glutes. They can be performed using a glute-ham raise machine or modified using a stability ball or bench.
How To Do Glute-Ham Raises?
- Position yourself on a glute-ham raise machine with your feet secured under the footpads and your thighs resting on the pad.
- Lower your torso towards the ground while maintaining a straight line from your head to your knees.
- Engage your hamstrings and glutes to lift your torso back up to the starting position.
- Control the movement throughout the entire range of motion to maximize muscle engagement.
Execution Tips Enhanced:
- Focus on squeezing your hamstrings and glutes at the top of the movement.
- Keep your core engaged to maintain stability and control.
- Adjust the footpad position to increase or decrease the difficulty of the exercise.
Why It Works Explained:
Glute-Ham Raises target the hamstrings and glutes by placing them under constant tension throughout the movement. The exercise involves both hip extension and knee flexion, which are primary functions of the hamstrings.
By controlling the descent and ascent of the body, Glute-Ham Raises effectively isolate and strengthen the hamstrings and glutes while also improving stability and coordination.
3. Lying Leg Curls
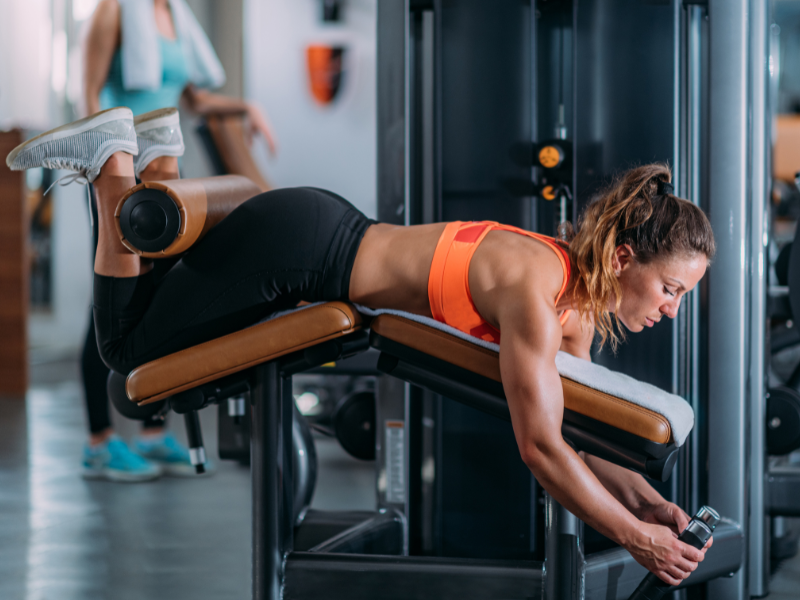

Lying Leg Curls are a popular isolation exercise for targeting the hamstrings. They effectively isolate the hamstrings while minimizing the involvement of other muscle groups.
How To Do Lying Leg Curls?
- Lie face down on a leg curl machine with your legs extended and the padded lever positioned above your ankles.
- Grasp the handles for stability and contract your hamstrings to curl the lever towards your glutes.
- Pause for a moment at the top of the movement, then slowly lower the lever back to the starting position.
- Maintain control throughout the exercise to maximize muscle engagement.
Execution Tips Enhanced:
- Keep your hips flat on the bench throughout the movement.
- Avoid using momentum to lift the weight; focus on controlled, deliberate movements.
- Adjust the machine settings to ensure proper alignment and range of motion.
Why It Works Explained:
Lying Leg Curls target the hamstrings by flexing the knee joint against resistance. This movement isolates the hamstrings while minimizing involvement of other muscle groups, allowing for focused activation and strengthening of the hamstrings.
By controlling the movement and maintaining proper form, Lying Leg Curls effectively target the hamstrings to promote muscle growth and strength.
4. Barbell Good Mornings
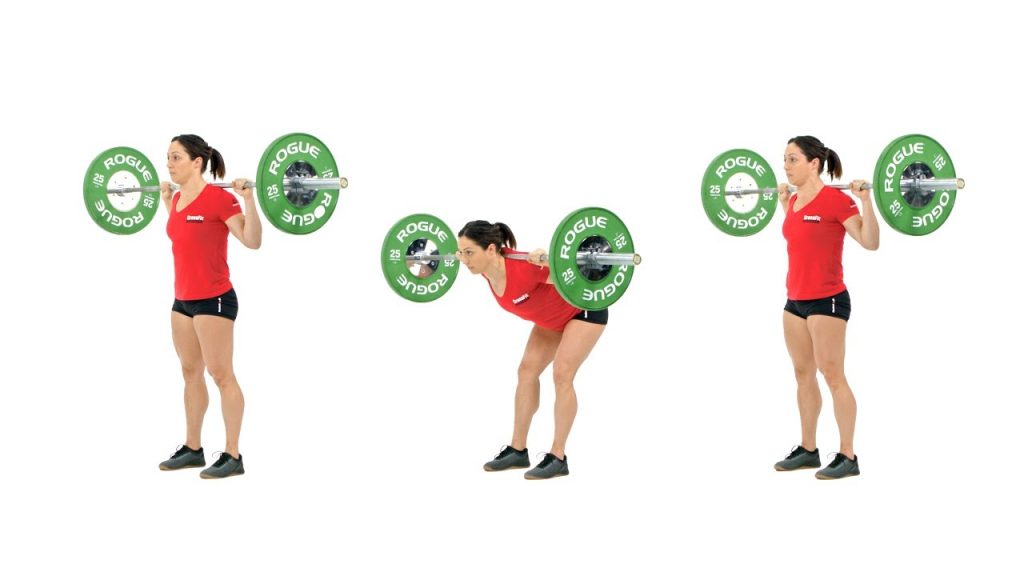

Barbell Good Mornings are a compound exercise that targets the hamstrings, lower back, and glutes. They involve a hip hinge movement pattern similar to Romanian Deadlifts but with the barbell positioned across the shoulders.
How To Do Good Mornings:
- Stand with feet shoulder-width apart and a barbell across your shoulders, resting behind your neck.
- Keep your back flat and chest up as you hinge at the hips, pushing your glutes back while bending forward at the waist.
- Lower your torso until you feel a stretch in your hamstrings, then return to the starting position by driving your hips forward.
- Maintain a slight bend in the knees throughout the movement and keep the barbell close to your body.
Execution Tips Enhanced:
- Start with light weights to master the movement pattern before progressing to heavier loads.
- Keep your core engaged and spine neutral throughout the exercise to minimize the risk of injury.
- Focus on feeling the stretch in your hamstrings as you lower your torso, then squeeze your glutes to return to the starting position.
Why It Works Explained:
Good Mornings target the hamstrings, lower back, and glutes by emphasizing hip hinge movement and posterior chain activation. The exercise places the hamstrings under tension throughout the movement, promoting strength and muscle growth.
Additionally, Good Mornings improve hip mobility and stability, making them a valuable exercise for overall lower body strength and function.
5. Single-Leg Romanian Deadlifts
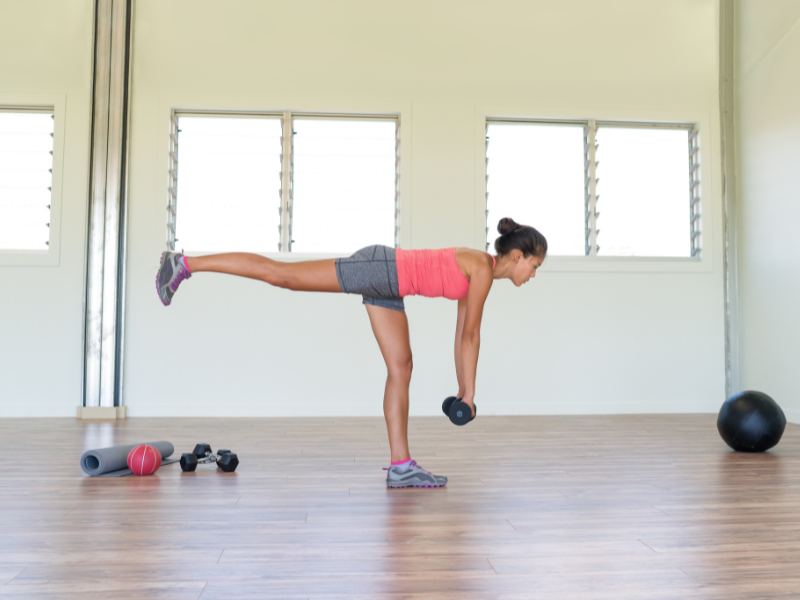

Single-Leg Romanian Deadlifts are a unilateral exercise that targets the hamstrings and glutes while also improving balance and stability. By isolating each leg individually, this exercise helps correct muscle imbalances between the left and right sides of the body.
How To Do Single-Leg Romanian Deadlifts:
- Stand on one leg with a slight bend in the knee and hold a dumbbell or kettlebell in one hand.
- Keeping your back flat and chest up, hinge at the hips and lower the weight towards the ground while extending the non-supporting leg behind you for balance.
- Keep the weight close to your body and maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement.
- Once you reach the bottom position, squeeze your glutes and hamstrings to return to the starting position.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions before switching to the other leg.
Execution Tips Enhanced:
- Focus on keeping your hips square and parallel to the ground throughout the movement.
- Keep your core engaged to maintain balance and stability.
- Start with body weight or light weights to master the movement before increasing resistance.
Why It Works Explained:
Single-Leg Romanian Deadlifts target the hamstrings and glutes while also improving balance, stability, and coordination. By isolating each leg individually, this exercise helps correct muscle imbalances and asymmetries between the left and right sides of the body.
The hip hinge movement pattern emphasizes hip extension, which is primarily driven by the hamstrings, making Single-Leg Romanian Deadlifts an effective exercise for strengthening and developing the posterior chain.
6. Swiss Ball Leg Curls
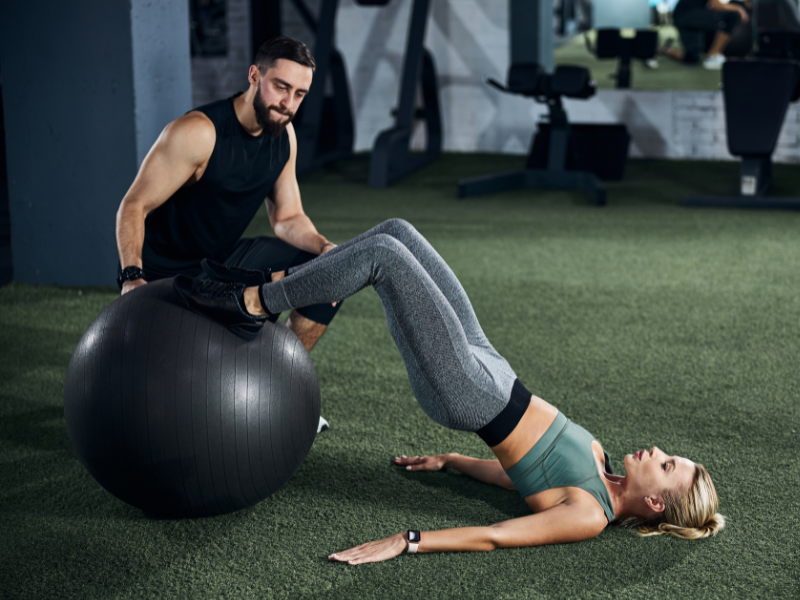

Swiss Ball Leg Curls are a challenging exercise that targets the hamstrings while also engaging the core and stabilizing muscles. Performing leg curls on a stability ball adds an element of instability, increasing the difficulty of the exercise and challenging stability and coordination.
How To Do Swiss Ball Leg Curls?
- Lie on your back with your arms by your sides and your heels on top of a stability ball.
- Lift your hips off the ground to form a straight line from your shoulders to your heels.
- Engage your core and hamstrings to bend your knees and roll the stability ball towards your glutes.
- Pause for a moment at the top of the movement, then slowly extend your legs to return to the starting position.
- Maintain control throughout the exercise to maximize muscle engagement and stability.
Execution Tips Enhanced:
- Keep your hips lifted and core engaged throughout the movement to maintain stability.
- Focus on using your hamstrings to roll the stability ball towards your glutes.
- Control the descent of the ball to prevent it from rolling away too quickly.
Why It Works Explained:
Swiss Ball Leg Curls target the hamstrings while also challenging stability and coordination. The unstable surface of the stability ball requires activation of the core and stabilizing muscles to maintain balance throughout the exercise. By bending the knees and rolling the ball towards the glutes, the hamstrings are engaged to perform knee flexion against resistance.
This makes Swiss Ball Leg Curls an effective exercise for strengthening the hamstrings while also improving core stability and balance.
7. Barbell Hip Thrusts
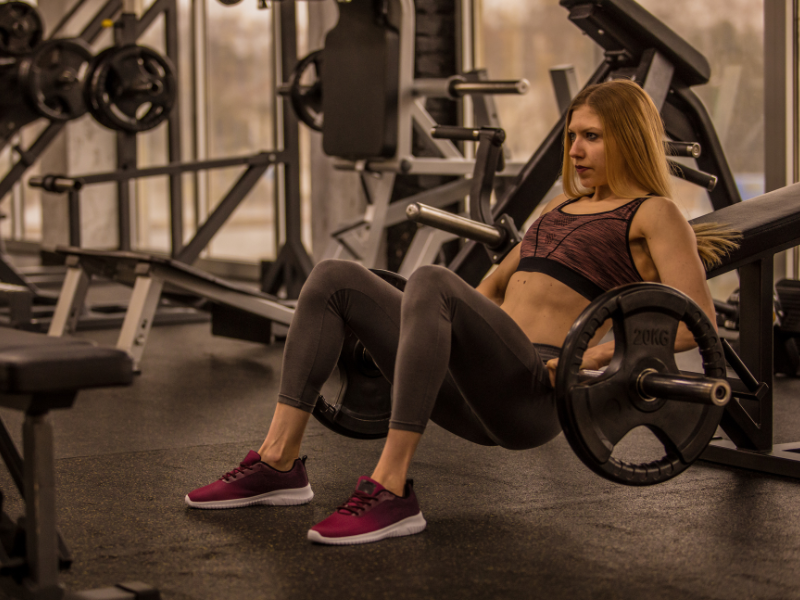

Barbell Hip Thrusts primarily target the glutes but also activate the hamstrings as secondary muscles. This exercise involves thrusting the hips upwards while seated on the ground with the upper back supported by a bench and a barbell positioned across the hips.
How To Do Barbell Hip Thrusts:
- Sit on the ground with your upper back against a bench and a barbell across your hips.
- Roll the barbell towards your hips and position it securely.
- Plant your feet flat on the ground, shoulder-width apart, and brace your core.
- Thrust your hips upwards by driving through your heels and squeezing your glutes.
- Pause at the top of the movement, then lower your hips back down with control.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Execution Tips Enhanced:
- Ensure that your shoulders are supported by the bench throughout the exercise to protect your spine.
- Focus on driving through your heels and engaging your glutes to lift the weight.
- Keep your core braced and avoid overarching your lower back.
Why It Works Explained:
Barbell Hip Thrusts primarily target the glutes, but they also engage the hamstrings as stabilizers and synergists. The hip extension movement pattern activates both the glutes and hamstrings, leading to increased strength and muscle development in these muscle groups.
By thrusting the hips upwards against resistance, Barbell Hip Thrusts effectively target the posterior chain while also improving hip strength and stability.
8. Kettlebell Swings
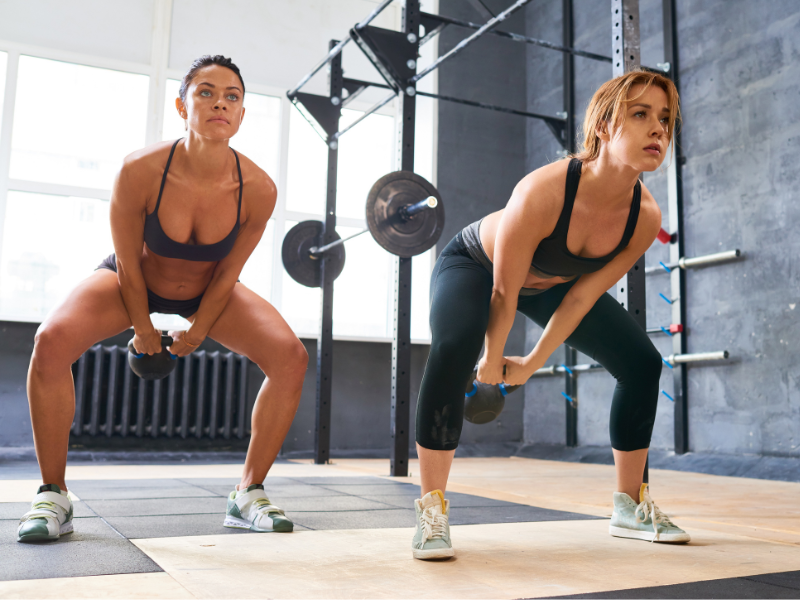

Kettlebell Swings are a dynamic exercise that primarily targets the posterior chain, including the hamstrings, glutes, and lower back. This explosive movement involves swinging a kettlebell between the legs and thrusting the hips forward to generate momentum.
How To Do Kettlebell Swings:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and hold a kettlebell with both hands in front of your body.
- Hinge at the hips and lower the kettlebell between your legs while keeping your back flat.
- Explosively thrust your hips forward and swing the kettlebell up to shoulder height.
- Allow the kettlebell to swing back down between your legs and repeat the movement in a fluid, continuous motion.
- Control the swing with your hips and engage your core throughout the exercise.
Execution Tips Enhanced:
- Focus on driving the movement with your hips rather than using your arms.
- Keep your back flat and chest up to maintain proper form and prevent injury.
- Start with a lighter kettlebell to master the movement before increasing the weight.
Why It Works Explained:
Kettlebell Swings target the hamstrings, glutes, and lower back by emphasizing hip hinge and explosive hip extension. The swinging motion generates momentum that requires the posterior chain muscles to work dynamically to control the movement.
By swinging the kettlebell between the legs and thrusting the hips forward, Kettlebell Swings effectively strengthen and develop the hamstrings while also improving power and athleticism.
9. Nordic Hamstring Curls
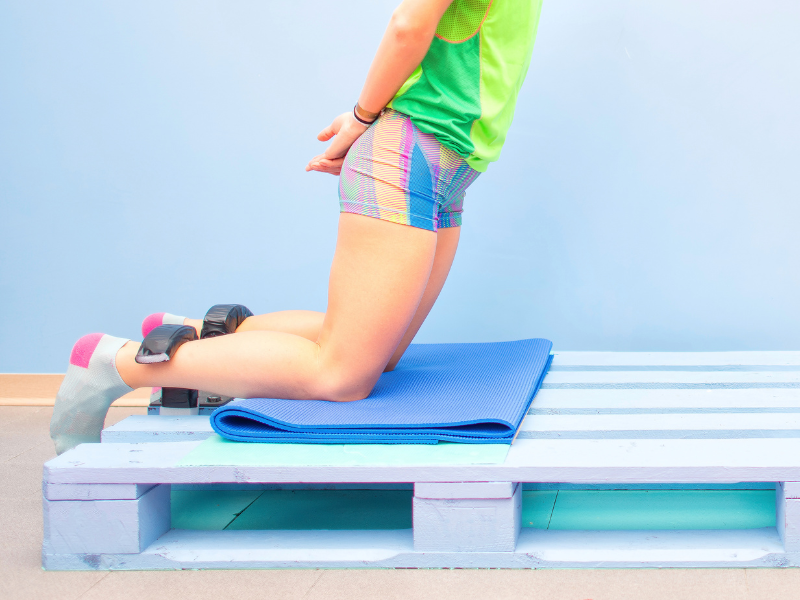

Nordic Hamstring Curls are an advanced bodyweight exercise that targets the hamstrings with a high degree of intensity. This exercise is challenging and requires significant hamstring strength and control to perform correctly.
How To Do Nordic Hamstring Curls?
- Kneel on a soft surface with your feet secured under a sturdy object or have a partner hold them down.
- Engage your core and slowly lower your torso towards the ground by bending at the knees.
- Control the descent until your body is nearly parallel to the ground.
- Push through your hamstrings to return to the starting position, using your arms for assistance if needed.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Execution Tips Enhanced:
- Keep your core engaged and maintain a straight line from your head to your knees throughout the movement.
- Lower your torso slowly and under control to maximize the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Gradually increase the range of motion as you build strength and improve flexibility.
Why It Works Explained:
Nordic Hamstring Curls target the hamstrings through both knee flexion and hip extension. The exercise places a high level of demand on the hamstrings, particularly during the eccentric (lowering) phase, which helps promote muscle hypertrophy and strength gains.
By controlling the descent and using the hamstrings to return to the starting position, Nordic Hamstring Curls effectively target and strengthen the hamstrings while also improving eccentric strength and control.
10. Bulgarian Split Squats

Bulgarian Split Squats are a unilateral lower body exercise that targets the hamstrings, quadriceps, and glutes. This challenging exercise also improves balance and stability, making it a valuable addition to any leg workout routine.
How To Do Bulgarian Split Squats?
- Stand facing away from a bench or elevated surface with one foot resting on it, and the other foot positioned slightly in front of you.
- Lower your body by bending your front knee until your thigh is parallel to the ground, while keeping your back straight and chest up.
- Push through your front heel to return to the starting position, keeping tension on the working leg throughout the movement.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions, then switch legs and repeat the exercise on the opposite side.
Execution Tips Enhanced:
- Maintain an upright torso and avoid leaning forward excessively.
- Focus on keeping your front knee aligned with your ankle to prevent it from collapsing inward.
- Use a controlled tempo, especially during the descent, to maximize muscle engagement and stability.
Why It Works Explained:
Bulgarian Split Squats target the hamstrings, quadriceps, and glutes while also engaging stabilizing muscles in the hips and core. The unilateral nature of the exercise helps address muscle imbalances and asymmetries between the left and right sides of the body.
By lowering the body into a single-leg squat position, Bulgarian Split Squats place a significant load on the hamstrings and quadriceps, promoting strength and muscle development.
Additionally, the elevated rear foot increases the range of motion, leading to greater muscle activation and growth in the working leg. Overall, Bulgarian Split Squats are an effective exercise for building lower body strength, stability, and muscle balance.
Common Hamstring Injuries and How to Prevent Them?
Hamstring injuries are among the most common injuries, particularly in athletes engaged in activities involving running, jumping, and sudden changes in direction.
Here are some common hamstring injuries and strategies to prevent them:
1. Strains:
Hamstring strains occur when the muscles or tendons are stretched beyond their capacity or torn. They can range from mild to severe and often result from inadequate warm-up, overuse, or muscle imbalances.
Prevention:
- Warm up properly before physical activity to increase blood flow to the muscles and improve flexibility.
- Incorporate dynamic stretches and movements specific to the hamstrings.
- Gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercise to avoid overloading the muscles.
- Include strength training exercises targeting the hamstrings, such as deadlifts and Romanian deadlifts, to improve muscle strength and resilience.
2. Tendinitis:
Hamstring tendinitis is inflammation of the hamstring tendons, usually near the attachment points at the pelvis or knee. It can result from overuse, repetitive stress, or sudden increases in training intensity.
Prevention:
- Ensure proper biomechanics and technique during activities that stress the hamstrings, such as running and jumping.
- Avoid sudden increases in training volume or intensity, and allow adequate rest and recovery between sessions.
- Incorporate cross-training activities that reduce stress on the hamstrings, such as swimming or cycling.
- Maintain flexibility and mobility in the hamstrings through regular stretching and mobility exercises.
3. Avulsion Injuries:
Avulsion injuries occur when the hamstring tendon pulls away from the bone, often resulting in a partial or complete tear. These injuries are typically seen in explosive movements, such as sprinting or jumping, and may require surgical intervention.
Prevention:
- Gradually progress training loads and intensity to minimize the risk of sudden, forceful contractions that can lead to avulsion injuries.
- Incorporate eccentric strengthening exercises, such as Nordic hamstring curls, to improve tendon resilience and prevent tears.
- Focus on proper landing mechanics during jumping and cutting movements to reduce stress on the hamstrings and associated tendons.
4. Repetitive Strain Injuries:
Repetitive strain injuries occur due to repeated stress on the hamstring muscles and tendons over time. They can result from poor biomechanics, inadequate recovery, or training errors.
Prevention:
- Pay attention to training volume, intensity, and recovery to prevent overuse injuries. Incorporate rest days and active recovery techniques, such as foam rolling and massage, to promote muscle recovery and reduce the risk of strain.
- Address any biomechanical issues or muscle imbalances through targeted strength and mobility exercises.
- Ensure proper footwear and equipment to support optimal movement patterns and reduce stress on the hamstrings.
By implementing these preventive strategies and maintaining a balanced approach to training, you can significantly reduce the risk of hamstring injuries and maintain optimal lower body health and function. Additionally, regular assessment of movement patterns, flexibility, and strength can also help identify potential risk factors and address them proactively.
How to Include Hamstring Exercises into Your Routine?
Incorporating hamstring exercises into your routine is essential for building strength, preventing injuries, and improving overall lower body function.
Here’s how you can effectively include hamstring exercises into your workout routine:
- Set Clear Goals: Determine your fitness goals and how incorporating hamstring exercises aligns with them. Whether you aim to increase strength, improve athletic performance, or enhance muscle definition, having clear objectives will guide your exercise selection and programming.
- Choose a Variety of Exercises: Select a variety of hamstring exercises that target the muscles from different angles and movement patterns. Include both compound exercises, such as Romanian deadlifts and Bulgarian split squats, and isolation exercises, like lying leg curls and Swiss ball leg curls, to ensure comprehensive muscle activation.
- Prioritize Compound Movements: Start your workout with compound hamstring exercises that recruit multiple muscle groups simultaneously. These exercises, such as deadlift variations and hip thrusts, are effective for building overall strength and muscle mass in the hamstrings while also engaging other lower-body muscles.
- Balance Your Routine: Ensure a balanced approach by incorporating hamstring exercises into your routine alongside exercises targeting other muscle groups, such as quadriceps, glutes, and calves. A well-rounded lower body routine promotes muscular balance, reduces the risk of overuse injuries, and supports functional movement patterns.
- Progressive Overload: Gradually increase the intensity, volume, or resistance of your hamstring exercises over time to promote continuous adaptation and progress. This can be achieved by adding weight, increasing repetitions, or adjusting exercise variations to challenge your muscles effectively.
- Include Recovery Days: Allow adequate rest and recovery between hamstring workouts to optimize muscle repair and growth. Incorporate active recovery strategies such as stretching, foam rolling, and mobility work to enhance circulation, reduce muscle soreness, and promote faster recovery.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body responds to hamstring exercises and adjust your routine accordingly. If you experience pain or discomfort, modify the exercise selection, technique, or intensity to prevent injury and promote long-term health.
- Consult a Professional: If you’re new to exercising or have specific fitness goals or concerns, consider consulting a certified personal trainer or physical therapist. They can provide personalized guidance, create a tailored workout plan, and ensure proper form and technique to maximize the effectiveness of your hamstring exercises.
You can effectively integrate hamstring exercises into your workout regimen and experience the benefits of improved lower body strength, performance, and overall fitness by incorporating these strategies into your routine.
Essential Takeaways
In conclusion, integrating hamstring exercises into your workout routine is crucial for promoting lower body strength, preventing injuries, and optimizing overall fitness. By incorporating a variety of exercises that target the hamstrings from different angles and movement patterns, you can effectively stimulate muscle growth and improve muscular balance.
Prioritizing compound movements, balancing your routine with exercises targeting other muscle groups, and progressively overloading your workouts are key strategies for achieving optimal results.
Additionally, listening to your body, allowing adequate recovery, and seeking professional guidance when needed are essential for ensuring safe and effective training. By following these principles and consistently incorporating hamstring exercises into your routine, you can enhance your athletic performance, support functional movement patterns, and achieve your fitness goals.
Key Points
- Strong hamstrings are crucial for overall leg strength, stability, and athletic performance.
- The hamstring muscle group consists of the Biceps femoris, Semitendinosus, and Semimembranosus, which play key roles in knee flexion, hip extension, and rotational movements.
- Benefits of strong hamstrings include improved athletic performance, reduced risk of injury, enhanced lower body strength, better posture, and flexibility.
- Incorporating hamstring exercises into your routine can help correct muscle imbalances, prevent injuries, and improve overall lower body function.
- Effective hamstring exercises include Romanian Deadlifts, Glute-Ham Raises, Lying Leg Curls, Good Mornings, Single-Leg Romanian Deadlifts, Swiss Ball Leg Curls, Barbell Hip Thrusts, Kettlebell Swings, Nordic Hamstring Curls, and Bulgarian Split Squats.
- To prevent common hamstring injuries, warm up properly, gradually increase training intensity, and address muscle imbalances through strength and mobility exercises.
- Include a variety of hamstring exercises in your routine, prioritize compound movements, and progressively overload your workouts to promote muscle growth and strength.
- Allow adequate rest and recovery between workouts, listen to your body, and seek professional guidance if needed to ensure safe and effective training.
- By consistently incorporating hamstring exercises into your routine and following these key principles, you can enhance lower body strength, performance, and overall fitness.
- Integrating hamstring exercises into your workout regimen supports muscular balance, reduces the risk of overuse injuries, and promotes optimal lower body health and function.
FAQs
How long does it take to strengthen your hamstrings?
The timeline for strengthening your hamstrings varies depending on factors such as your current fitness level, consistency of training, and individual factors like genetics and age.
Generally, noticeable improvements in hamstring strength can be seen within a few weeks to a couple of months for beginners or those starting a new exercise routine.
Here’s a general guideline:
- For beginners: You might start seeing noticeable improvements in hamstring strength within 4-8 weeks of consistent training.
- For intermediate exercisers: You could see results in 2-4 weeks.
- For advanced athletes: You might refine your strength and power within 1-2 weeks.
However, achieving significant gains in strength and muscle mass may take several months to a year of consistent training.
It’s important to approach hamstring strengthening with
- Patience,
- Consistency,
- A long-term mindset,
- Focusing on progressive overload,
- Proper technique,
- Adequate recovery to optimize results.
If you have specific goals or concerns, consulting with a fitness professional can provide personalized guidance tailored to your needs.
Can you train your hamstrings every day?
Training hamstrings every day may not be ideal for most individuals due to the risk of overtraining and potential injury. Hamstring muscles, like all muscles, require adequate rest and recovery time to repair and grow stronger after intense workouts.
Overtraining the hamstrings can lead to
- Muscle fatigue,
- Decreased performance,
- An increased risk of strains or tears.
Instead, it’s recommended to incorporate hamstring exercises into your workout routine two to three times per week, allowing at least one day of rest between sessions to promote optimal recovery.
Additionally, focusing on proper nutrition, hydration, and quality sleep can further support muscle recovery and growth. If you’re considering increasing training frequency or have specific concerns, consult with a fitness professional to design a safe and effective training program tailored to your individual needs and goals.
How long can it take to loosen hamstrings?
The time it takes to loosen tight hamstrings can vary depending on factors such as the severity of tightness, individual flexibility, and consistency of stretching. While some individuals may experience noticeable improvements within a few weeks, others may require several months of dedicated effort to achieve significant gains in flexibility.
Consistent stretching and mobility exercises, combined with proper technique and gradual progression, are key to improving hamstring flexibility safely and effectively. It’s important to listen to your body, avoid pushing stretches to the point of pain, and be patient with the process.
If you have specific concerns or limitations, consulting with a qualified fitness or healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance tailored to your needs.
Can you build hamstrings without weights?
Yes, it is possible to build strong and defined hamstrings without using weights. While traditional weightlifting exercises such as deadlifts and Romanian deadlifts are effective for hamstring development, there are several bodyweight and resistance band exercises that can effectively target and strengthen the hamstrings.
Examples include bodyweight hamstring curls, glute-ham raises, Nordic hamstring curls, single-leg Romanian deadlifts, and resistance band leg curls. These exercises utilize your body weight or resistance bands to create tension in the hamstrings, promoting muscle growth and strength.
Additionally, incorporating plyometric exercises like jump squats and lunge jumps can further enhance hamstring strength and power.
Consistency, proper technique, and progressive overload are key principles to follow when building hamstrings without weights. If you have specific fitness goals or concerns, consulting with a fitness professional can help tailor a training program to suit your needs and maximize results.
What movements do the hamstrings control?
The hamstrings play a crucial role in various movements involving the lower body. They are primarily responsible for flexing the knee joint, which involves bringing the heel towards the buttocks. This action is essential for activities such as walking, running, jumping, and climbing stairs.
Additionally, the hamstrings assist in extending the hip joint, which involves moving the thigh backwards. This movement pattern is particularly important during activities like sprinting, cycling, and bending forward at the hips.
Overall, the hamstrings are involved in both knee flexion and hip extension, making them vital for functional movements and athletic performance. Regular strength training and flexibility exercises targeting the hamstrings can help improve muscle function, reduce the risk of injury, and enhance overall lower body performance.

ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Follow Valen Steven for a dose of fitness enthusiasm, evidence-based advice, and a roadmap to achieving your health and wellness goals.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Dive into a world of fitness and wellness with our exclusive newsletter! Sign up now and receive weekly power-packs of fitness wisdom




